The Evolution of Computing: From Quartz to Quantum
- witwavesblog
- Sep 5, 2024
- 3 min read
The field of computing has evolved dramatically over the past century, from the mechanical devices of the 1930s to today’s advanced processors. Here’s a deep dive into how computers work, categorized into different types of processing units and technologies that power them.
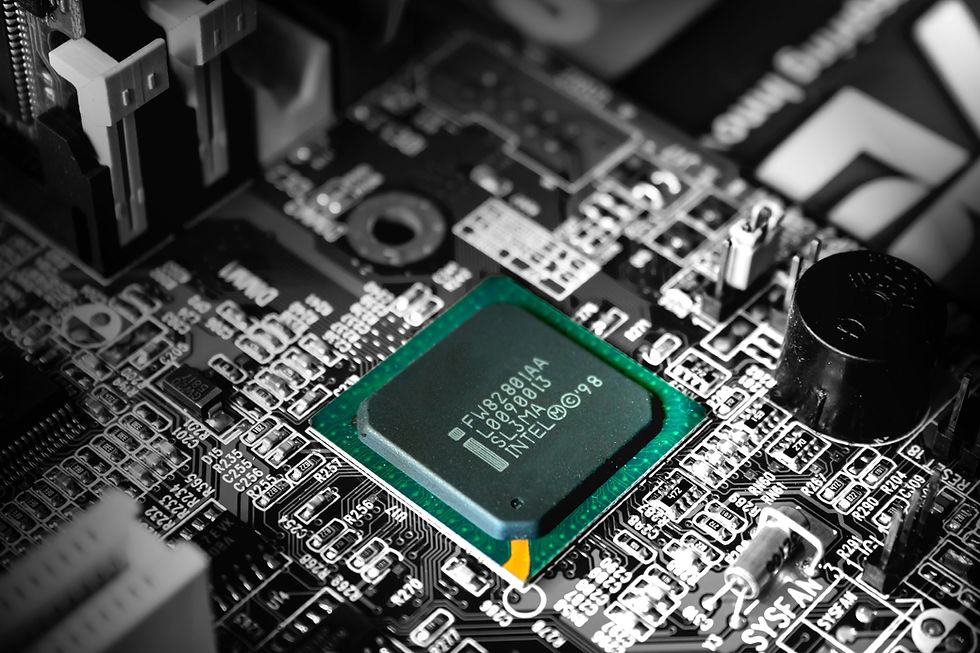
From Quartz to Silicon: The Foundations of Computing
In distant lands, quartz crystals rich in silicon dioxide are extracted and refined into silicon substrates, which are integral to modern computing. This material forms the base of most microchips, as it can be both a conductor and insulator. These chips become the foundation for every computer we use today, with engineers using advanced processes to inscribe billions of circuits. The result? Modern computers capable of incomprehensible levels of processing.
The First Programmable Computer: Z1
Computing's journey began in 1936 when Conrad Zuse created the first programmable computer, the Z1. Built in his mother’s basement, the Z1 could perform Boolean algebra and other calculations but was destroyed during World War II. Despite its destruction, this marked a critical moment in computing history. The Z1 operated at one instruction per second, far slower than today’s CPUs, which run at gigahertz speeds.
The Game-Changing Transistor
The invention of the transistor in 1947 changed everything. Transistors, semiconductors that can switch electrical signals, became the essential component of modern processors. Transistors can represent binary values, where "1" means current passes through and "0" means it doesn’t. The development of integrated circuits in 1958 allowed multiple transistors to be placed on a single silicon chip, paving the way for microprocessors.
CPUs: The Brain of Modern Computers
In 1971, Intel released the first commercial microprocessor, marking the birth of the Central Processing Unit (CPU). CPUs act as the brain of the computer, executing programs, managing hardware, and running the operating system. Modern CPUs have multiple cores, allowing them to perform parallel processing, making it possible to run multiple programs at once. Despite their power, there are limits to what CPUs can achieve, leading to the development of specialized processing units.
GPUs: Graphics Processing Power
When it comes to rendering complex graphics or training AI models, Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) are the go-to. With thousands of cores, GPUs are optimized for parallel computations, which makes them essential for tasks like video rendering or large-scale machine learning. NVIDIA’s GPUs have become particularly valuable in both gaming and AI, powering industries beyond just graphics.
TPUs: Specialized for AI
Google introduced Tensor Processing Units (TPUs) in 2016, chips designed specifically for AI and deep learning tasks. TPUs handle matrix multiplication efficiently, which is crucial for training neural networks on large datasets. TPUs are used in massive data centers and cloud computing platforms, driving advancements in AI technologies.
DPUs: The Future of Data Centers
The Data Processing Unit (DPU) is designed for managing large-scale data. These chips handle networking, security, and data storage functions, offloading these tasks from the CPU. DPUs are becoming critical in cloud computing environments, allowing for more efficient data management and processing.
Quantum Computing: The Next Frontier
While CPUs, GPUs, TPUs, and DPUs dominate today, the future lies in Quantum Processing Units (QPUs). Quantum computers use qubits, which can exist in multiple states simultaneously, allowing for exponential processing power. Though still in early development, quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize encryption, AI, and scientific simulations, unlocking new possibilities previously unimaginable.
Conclusion: A Constantly Evolving Landscape
From the Z1 to quantum processors, computing has come a long way in a short time. Each innovation has built upon the last, with new processing units being developed to meet the increasing demand for more power and efficiency. As we continue to push the boundaries of technology, it’s exciting to imagine what the next 100 years will bring.





Comments